
If you’ve ever found yourself in the grocery store wondering whether you should pick up a yam or a sweet potato for your next recipe, you’re not alone! Despite the fact that the names are commonly used interchangeably, yams and sweet potatoes are quite different—both in origin and in taste.

When it comes to yams and sweet potatoes, one of the most significant differences lies in their origins and botanical families. Although these tubers may look somewhat similar on the outside, they come from entirely different parts of the world and belong to distinct plant families.

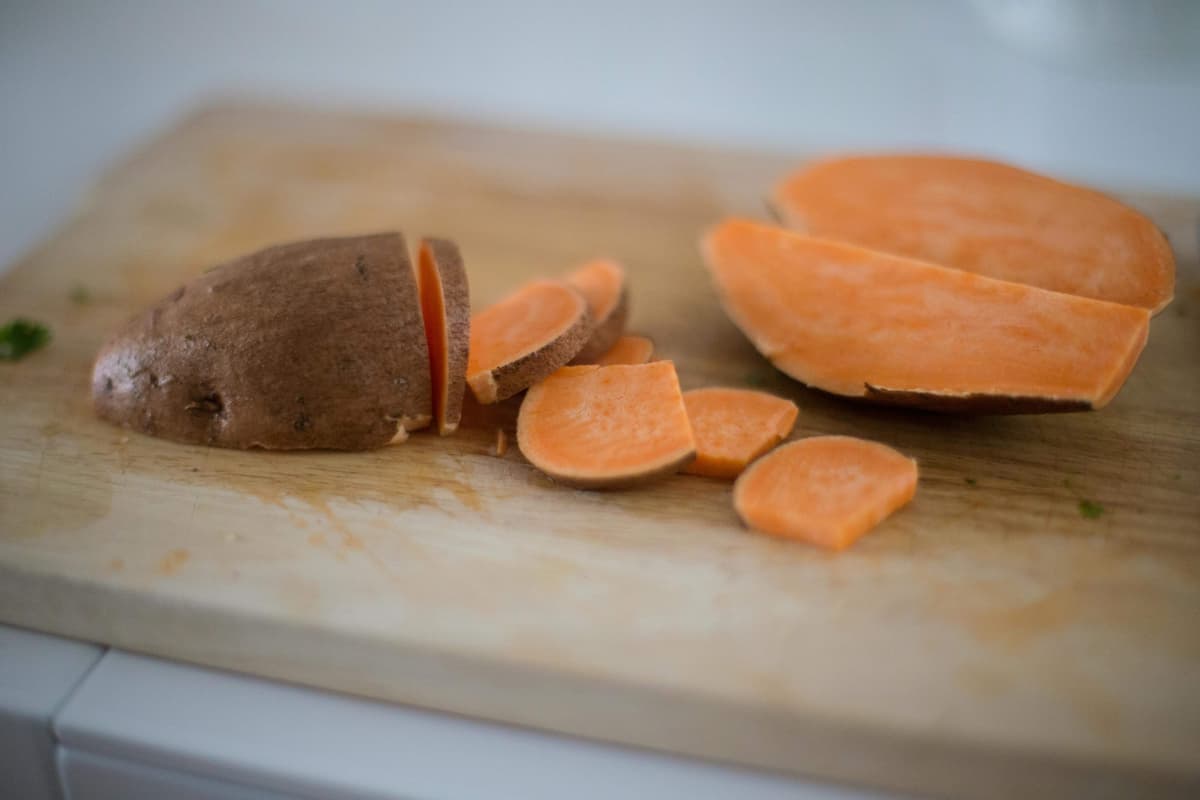
Sweet potatoes (Ipomoea batatas) trace their origins back to Central and South America. They are members of the Convolvulaceae family, commonly known as the morning glory family. This connection to the morning glory flower might surprise you, but it explains the vibrant, trailing vines that sweet potato plants produce.
Sweet potatoes have been cultivated for thousands of years, with early records of their use in Peru dating back as far as 8,000 years. Over time, sweet potatoes spread across the globe, becoming a staple in many cuisines, particularly in the United States, where they are often featured in traditional dishes like casseroles and pies.
Sweet potatoes come in a variety of colors, including orange, white, yellow, and even purple. Each variety offers a slightly different flavor profile and texture, making sweet potatoes incredibly versatile in cooking.
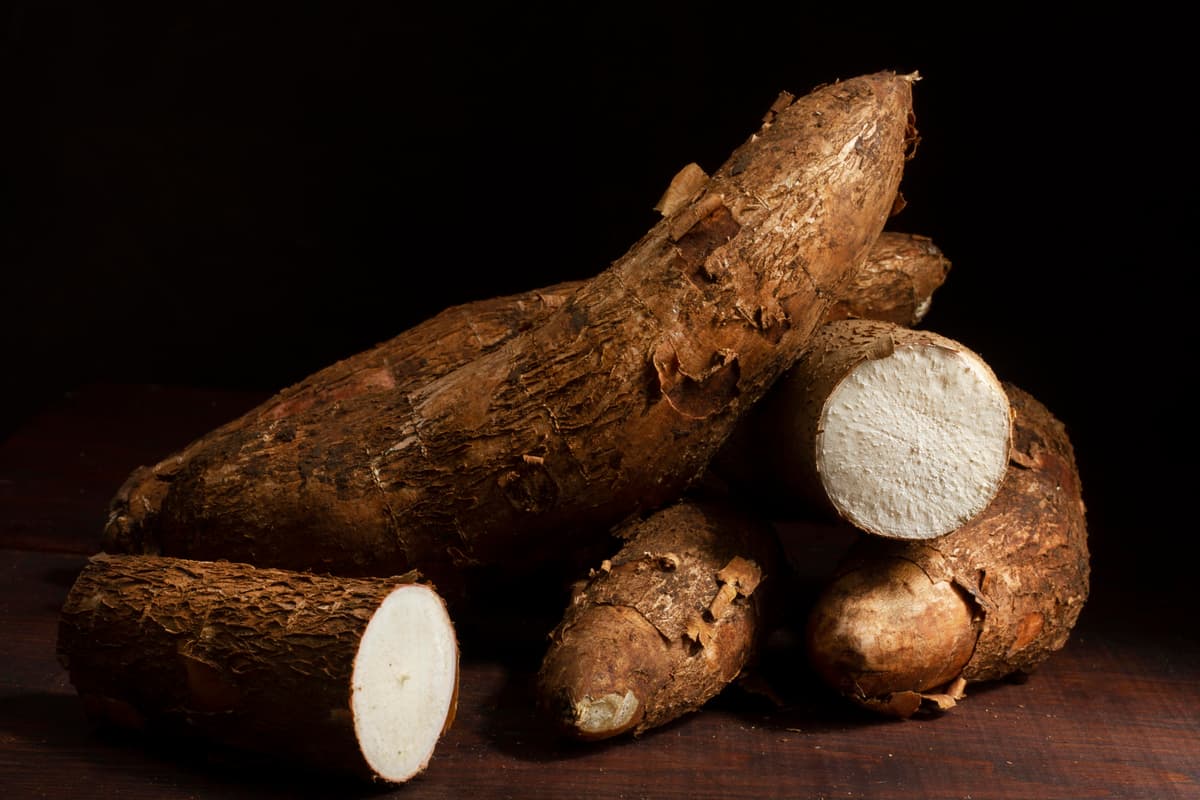
Yams (Dioscorea spp.), on the other hand, have a much different origin story. True yams are native to Africa and Asia and are a staple food in many tropical regions. Yams belong to the Dioscoreaceae family, which sets them apart from sweet potatoes on a botanical level. Unlike sweet potatoes, which are generally small- to medium-sized, yams can grow to be enormous.
In Africa, yams hold significant cultural importance and are often celebrated in festivals, particularly during the harvest season. They are also a crucial source of sustenance in many countries, providing essential carbohydrates and calories to the diet.
Yams and sweet potatoes may both be tuberous roots, but their distinct origins and familial ties reflect the diversity of plant life and culinary traditions across the world.
When it comes to distinguishing between yams and sweet potatoes, appearance and texture are two of the most noticeable differences. Despite their similar names and some overlapping uses in the kitchen, they can be quite distinct in look and feel.
Sweet potatoes are often easily recognized by their smooth skin and vibrant flesh. The skin of a sweet potato is generally thin and can range in color from pale yellow to dark brown, depending on the variety. The flesh inside is equally diverse, with common colors being orange, white, yellow, and even purple.
Yams, in contrast, have a much rougher and more rugged appearance. The skin of a true yam is thick, rough, and often described as bark-like. This tough, scaly exterior is one of the key features that sets yams apart from sweet potatoes. The flesh inside a yam can vary in color from white to purple to reddish, but it is typically drier and starchier than that of sweet potatoes.
One easy way to tell the difference between yams and sweet potatoes is by looking at their shape and skin texture. Sweet potatoes tend to have a more uniform, cylinder-like shape with tapered ends, while yams are often more irregular in shape and size. The smooth, thin skin of a sweet potato is in stark contrast to the rough, scaly skin of a yam.
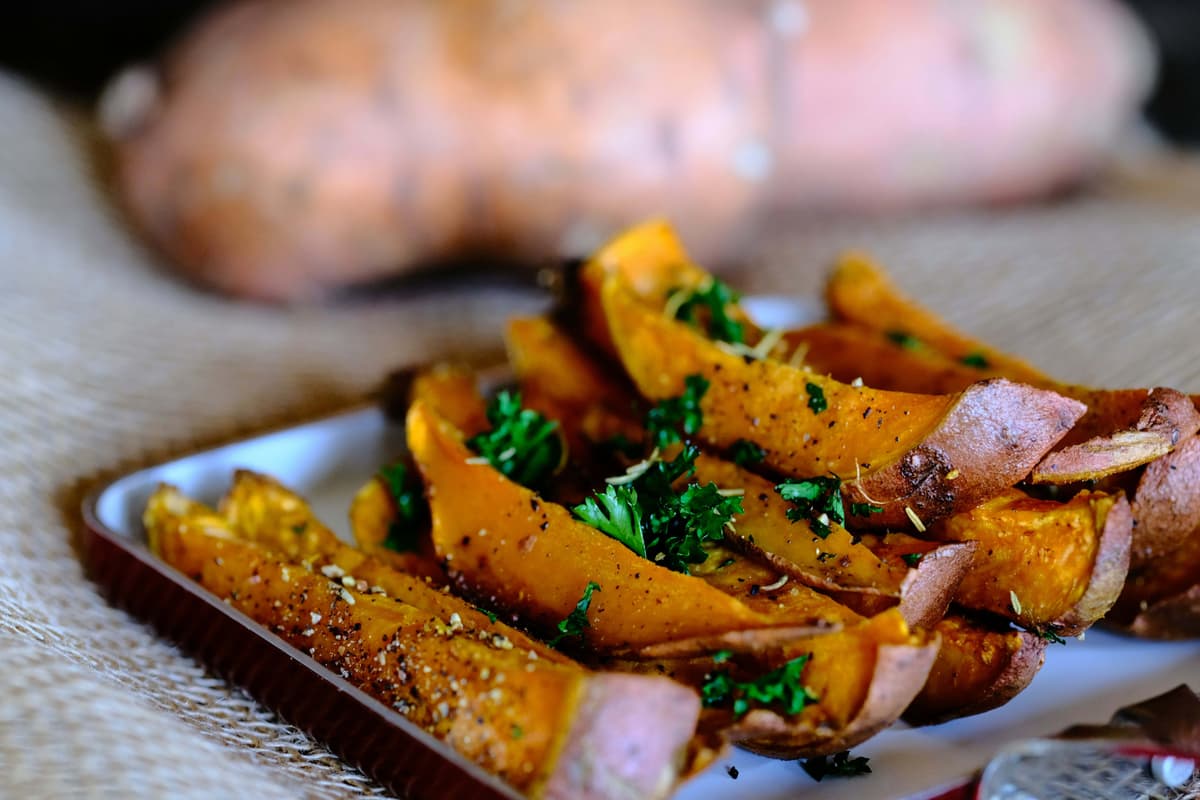
Sweet potatoes are known for their naturally sweet flavor, which becomes even more pronounced when they are cooked. The sweetness of sweet potatoes is one of the reasons they are so popular in both savory and dessert recipes. When baked, roasted, or boiled, the flesh of a sweet potato becomes soft, moist, and almost creamy, making it a perfect ingredient for dishes like sweet potato pie, casseroles, and even fries.
Yams, on the other hand, offer a more neutral and earthy flavor profile, which is less sweet and more starchy compared to sweet potatoes. This starchy quality makes yams an excellent ingredient for savory dishes, especially in African, Caribbean, and Asian cuisines, where they are a staple food. Yams can be boiled, mashed, roasted, or fried, and they are often used in stews, soups, and other hearty dishes where they absorb the flavors of spices and other ingredients.
The dry, starchy texture of yams requires them to be cooked for longer periods, often with added moisture, to achieve a tender consistency. In West African cuisine, for example, yams are often pounded into a smooth, dough-like consistency known as “fufu,” which is used as a base to soak up rich stews and soups. Because of their less sweet and more robust texture, yams are less likely to be used in dessert dishes and are more often found in savory applications where their starchiness can be highlighted.
Yams and sweet potatoes are both nutritious, but they offer different health benefits due to their distinct nutritional profiles.
Sweet potatoes are nutritional powerhouses, especially when it comes to their vitamin content. One of the most notable nutrients in sweet potatoes is beta-carotene, a powerful antioxidant that gives the orange-fleshed varieties their vibrant color. Beta-carotene is a precursor to vitamin A, which is essential for maintaining healthy vision, immune function, and skin health. Just one medium-sized orange sweet potato can provide more than 100% of the daily recommended intake of vitamin A.
Sweet potatoes have a lower glycemic index (GI) compared to regular white potatoes, which means they have a more gradual impact on blood sugar levels. This makes them a favorable option for people managing blood sugar levels, such as those with diabetes.
Yams, while less sweet than sweet potatoes, are rich in complex carbohydrates, which provide a steady source of energy. The starchy nature of yams makes them particularly satisfying and filling. Yams are also a good source of dietary fiber, which supports digestive health and helps regulate blood sugar levels.
One of the key nutrients found in yams is potassium, which is crucial for maintaining healthy blood pressure and heart function. Yams also contain manganese, a mineral that plays a role in bone health and metabolism. Yams also contain some vitamin C, though in lower amounts compared to sweet potatoes, and are a good source of B vitamins like vitamin B6.
Telling the difference between yams and sweet potatoes can be tricky, especially since the terms are often used interchangeably in grocery stores. However, there are some clear visual and textural cues that can help you identify each one accurately. Here’s a guide to help you distinguish between yams and sweet potatoes the next time you’re in the produce aisle.
Sweet Potatoes:
Yams:
Sweet Potatoes:
Yams:
Understanding the differences between these two tubers not only helps in making informed choices at the grocery store but also allows you to appreciate the unique culinary and cultural significance each brings to the table. Whether you’re looking to add a sweet and nutritious side to your meal or a hearty, starchy base for a stew, knowing how to distinguish between yams and sweet potatoes will help you pick the perfect ingredient every time.

If you’re one of the millions of people who have celiac disease or gluten sensitivities, you know that searching for gluten-free food can be an added dietary challenge. It takes effort to find which foods are safe to eat and which foods can cause negative reactions. Despite this challenge, it is still possible to enjoy …

Does eating a healthy diet require you to give up fast food? Not always. If you choose wisely while placing your fast food order, you can incorporate occasional fast food consumption into a balanced diet. Keep these recommendations in mind. Next time you head to your local fast-food restaurant, these five suggestions can help you make …

Wheatgrass, the newly sprouted grass of the common wheat plant Triticum aestivum, has been revered as a potent health elixir with many benefits. Known for its vibrant green color and impressive nutritional profile, wheatgrass is packed with vitamins, minerals, enzymes, and amino acids. This nutrient-dense superfood has been praised for its detoxifying properties, immune-boosting capabilities, …